算法数据结构
1 实现一个链表结构
链表结构
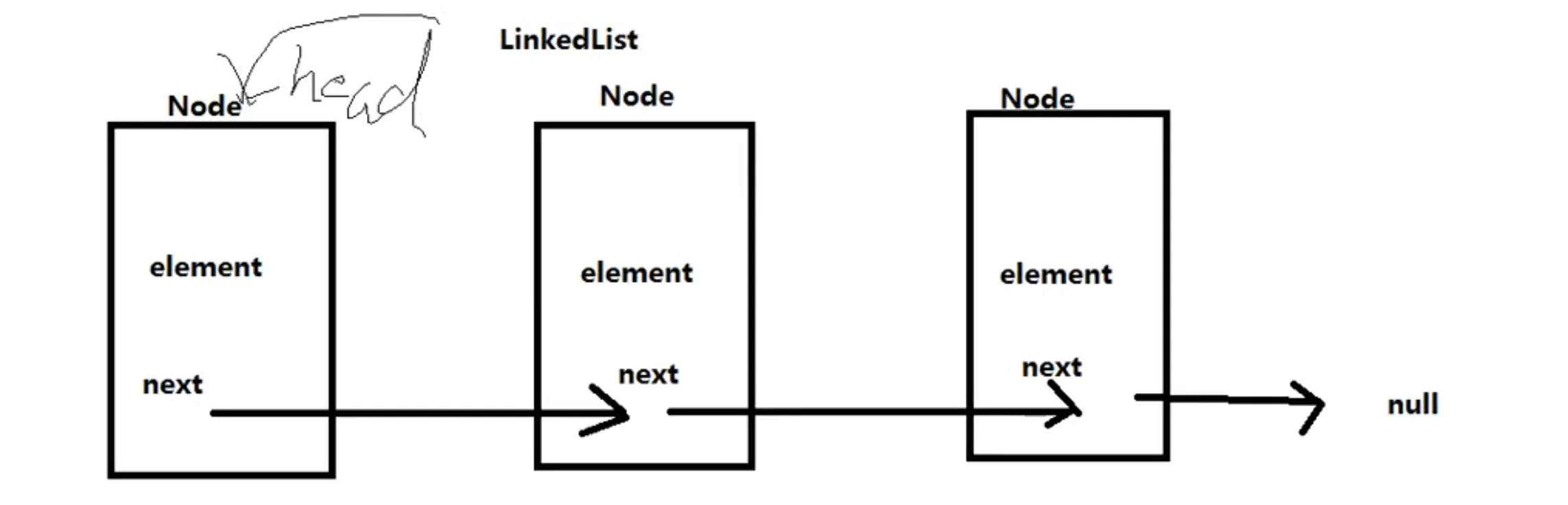
看图理解next层级
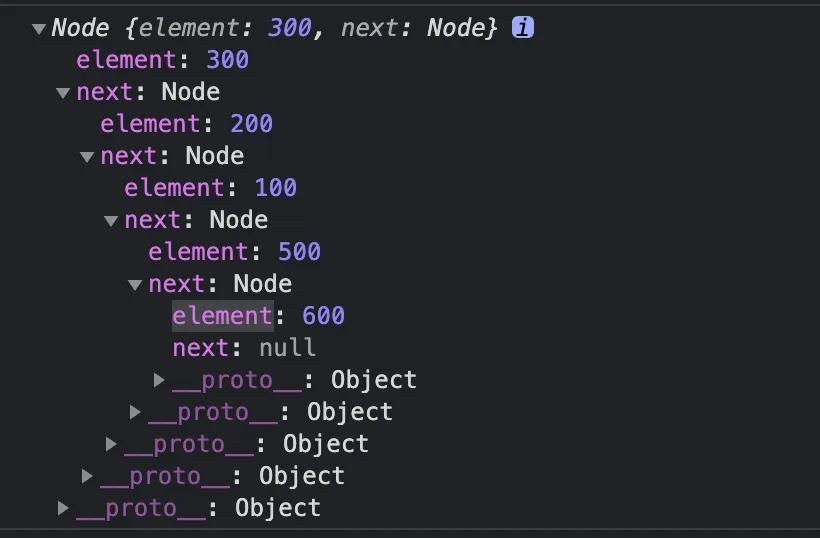
// 链表 从头尾删除、增加 性能比较好
// 分为很多类 常用单向链表、双向链表
// js模拟链表结构:增删改查
// node节点
class Node {
constructor(element,next) {
this.element = element
this.next = next
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null // 默认应该指向第一个节点
this.size = 0 // 通过这个长度可以遍历这个链表
}
// 增加O(n)
add(index,element) {
if(arguments.length === 1) {
// 向末尾添加
element = index // 当前元素等于传递的第一项
index = this.size // 索引指向最后一个元素
}
if(index < 0 || index > this.size) {
throw new Error('添加的索引不正常')
}
if(index === 0) {
// 直接找到头部 把头部改掉 性能更好
let head = this.head
this.head = new Node(element,head)
} else {
// 获取当前头指针
let current = this.head
// 不停遍历 直到找到最后一项 添加的索引是1就找到第0个的next赋值
for (let i = 0; i < index-1; i++) { // 找到它的前一个
current = current.next
}
// 让创建的元素指向上一个元素的下一个
// 看图理解next层级
current.next = new Node(element,current.next) // 让当前元素指向下一个元素的next
}
this.size++;
}
// 删除O(n)
remove(index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
throw new Error('删除的索引不正常')
}
this.size--
if(index === 0) {
let head = this.head
this.head = this.head.next // 移动指针位置
return head // 返回删除的元素
}else {
let current = this.head
for (let i = 0; i < index-1; i++) { // index-1找到它的前一个
current = current.next
}
let returnVal = current.next // 返回删除的元素
// 找到待删除的指针的上一个 current.next.next
// 如删除200, 100=>200=>300 找到200的上一个100的next的next为300,把300赋值给100的next即可
current.next = current.next.next
return returnVal
}
}
// 查找O(n)
get(index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
throw new Error('查找的索引不正常')
}
let current = this.head
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next
}
return current
}
}
var ll = new LinkedList()
ll.add(0,100) // Node { ellement: 100, next: null }
ll.add(0,200) // Node { element: 200, next: Node { element: 100, next: null } }
ll.add(1,500) // Node {element: 200,next: Node { element: 100, next: Node { element: 500, next: null } } }
ll.add(300)
ll.remove(0)
console.log(ll.get(2),'get')
console.log(ll.head)
module.exports = LinkedList
2 实现一个队列
基于链表结构实现队列
const LinkedList = require('./实现一个链表结构')
// 用链表默认使用数组来模拟队列,性能更佳
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.ll = new LinkedList()
}
// 向队列中添加
offer(elem) {
this.ll.add(elem)
}
// 查看第一个
peek() {
return this.ll.get(0)
}
// 队列只能从头部删除
remove() {
return this.ll.remove(0)
}
}
var queue = new Queue()
queue.offer(1)
queue.offer(2)
queue.offer(3)
var removeVal = queue.remove(3)
console.log(queue.ll,'queue.ll')
console.log(removeVal,'queue.remove')
console.log(queue.peek(),'queue.peek')
3 递归反转链表
// node节点
class Node {
constructor(element,next) {
this.element = element
this.next = next
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null // 默认应该指向第一个节点
this.size = 0 // 通过这个长度可以遍历这个链表
}
// 增加O(n)
add(index,element) {
if(arguments.length === 1) {
// 向末尾添加
element = index // 当前元素等于传递的第一项
index = this.size // 索引指向最后一个元素
}
if(index < 0 || index > this.size) {
throw new Error('添加的索引不正常')
}
if(index === 0) {
// 直接找到头部 把头部改掉 性能更好
let head = this.head
this.head = new Node(element,head)
} else {
// 获取当前头指针
let current = this.head
// 不停遍历 直到找到最后一项 添加的索引是1就找到第0个的next赋值
for (let i = 0; i < index-1; i++) { // 找到它的前一个
current = current.next
}
// 让创建的元素指向上一个元素的下一个
// 看图理解next层级 
current.next = new Node(element,current.next) // 让当前元素指向下一个元素的next
}
this.size++;
}
// 删除O(n)
remove(index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
throw new Error('删除的索引不正常')
}
this.size--
if(index === 0) {
let head = this.head
this.head = this.head.next // 移动指针位置
return head // 返回删除的元素
}else {
let current = this.head
for (let i = 0; i < index-1; i++) { // index-1找到它的前一个
current = current.next
}
let returnVal = current.next // 返回删除的元素
// 找到待删除的指针的上一个 current.next.next
// 如删除200, 100=>200=>300 找到200的上一个100的next的next为300,把300赋值给100的next即可
current.next = current.next.next
return returnVal
}
}
// 查找O(n)
get(index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
throw new Error('查找的索引不正常')
}
let current = this.head
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next
}
return current
}
reverse() {
const reverse = head=>{
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return head
}
let newHead = reverse(head.next)
// 从这个链表的最后一个开始反转,让当前下一个元素的next指向自己,自己指向null
// 
// 刚开始反转的是最后两个
head.next.next = head
head.next = null
return newHead
}
return reverse(this.head)
}
}
let ll = new LinkedList()
ll.add(1)
ll.add(2)
ll.add(3)
ll.add(4)
// console.dir(ll,{depth: 1000})
console.log(ll.reverse())
4 二叉树搜索
// 二叉搜索树
class Node {
constructor(element, parent) {
this.parent = parent // 父节点
this.element = element // 当前存储内容
this.left = null // 左子树
this.right = null // 右子树
}
}
class BST {
constructor(compare) {
this.root = null // 树根
this.size = 0 // 树中的节点个数
this.compare = compare || this.compare
}
compare(a,b) {
return a - b
}
add(element) {
if(this.root === null) {
this.root = new Node(element, null)
this.size++
return
}
// 获取根节点 用当前添加的进行判断 放左边还是放右边
let currentNode = this.root
let compare
let parent = null
while (currentNode) {
compare = this.compare(element, currentNode.element)
parent = currentNode // 先将父亲保存起来
// currentNode要不停的变化
if(compare > 0) {
currentNode = currentNode.right
} else if(compare < 0) {
currentNode = currentNode.left
} else {
currentNode.element = element // 相等时 先覆盖后续处理
}
}
let newNode = new Node(element, parent)
if(compare > 0) {
parent.right = newNode
} else if(compare < 0) {
parent.left = newNode
}
this.size++
}
}

// 测试
var bst = new BST((a,b)=>b.age-a.age) // 模拟sort方法
bst.add({age: 10})
bst.add({age: 8})
bst.add({age:19})
bst.add({age:20})
bst.add({age: 5})
console.log(bst)